Download Fortinet.NSE7_EFW-7.2.VCEplus.2024-02-13.20q.tqb
| Vendor: | Fortinet |
| Exam Code: | NSE7_EFW-7.2 |
| Exam Name: | Fortinet NSE 7 - Enterprise Firewall 7-2 |
| Date: | Feb 13, 2024 |
| File Size: | 2 MB |
| Downloads: | 2 |
Demo Questions
Question 1
Which statement about network processor (NP) offloading is true?
- For TCP traffic FortiGate CPU offloads the first packets of SYN/ACK and ACK of the three-way handshake to NP
- The NP provides IPS signature matching
- You can disable the NP for each firewall policy using the command np-acceleration st to loose.
- The NP checks the session key or IPSec SA
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
Option A is correct because the FortiGate CPU offloads the first packets of TCP sessions to the NP for faster connection establishment and reduced CPU load1.This feature is called TCP offloading and it is enabled by default on FortiGate models with NP6 or higher2.Option B is incorrect because the NP does not provide IPS signature matching.The NP only handles the packet forwarding and encryption/decryption functions, while the IPS signature matching is performed by the content processor (CP) or the CPU3.Option C is incorrect because the command to disable the NP for each firewall policy isset np-acceleration disable, notset np-acceleration st to loose4.This command can be used to prevent certain traffic types from being offloaded to the NP, such as multicast, broadcast, or non-IP packets5.Option D is incorrect because the NP does not check the session key or IPSec SA. The NP only offloads the IPSec encryption/decryption and tunneling functions, while the session key and IPSec SA are managed by the CPU.Reference: 1: TCP offloading2: Network processors (NP6, NP6XLite, NP6Lite, and NP4)3: Content processors (CP9, CP9XLite, CP9Lite)4: Disabling NP offloading for firewall policies5: NP hardware acceleration alters packet flow: IPSec VPN concepts Option A is correct because the FortiGate CPU offloads the first packets of TCP sessions to the NP for faster connection establishment and reduced CPU load1.This feature is called TCP offloading and it is enabled by default on FortiGate models with NP6 or higher2.
Option B is incorrect because the NP does not provide IPS signature matching.The NP only handles the packet forwarding and encryption/decryption functions, while the IPS signature matching is performed by the content processor (CP) or the CPU3.
Option C is incorrect because the command to disable the NP for each firewall policy isset np-acceleration disable, notset np-acceleration st to loose4.This command can be used to prevent certain traffic types from being offloaded to the NP, such as multicast, broadcast, or non-IP packets5.
Option D is incorrect because the NP does not check the session key or IPSec SA. The NP only offloads the IPSec encryption/decryption and tunneling functions, while the session key and IPSec SA are managed by the CPU.
Reference:
1: TCP offloading
2: Network processors (NP6, NP6XLite, NP6Lite, and NP4)
3: Content processors (CP9, CP9XLite, CP9Lite)
4: Disabling NP offloading for firewall policies
5: NP hardware acceleration alters packet flow
: IPSec VPN concepts
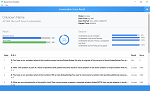
Question 2
Exhibit.
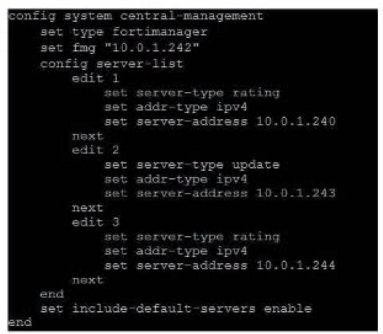
Refer to exhibit, which shows a central management configuration
Which server will FortiGate choose for web filler rating requests if 10.0.1.240 is experiencing an outage?
- Public FortiGuard servers
- 10.0.1.242
- 10.0.1.244
- 10.0.1.243
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
In the event of an outage at 10.0.1.240, the FortiGate will choose the next server in the sequence for web filter rating requests, which is 10.0.1.244 according to the configuration shown in the exhibit. This is because the server list is ordered by priority, and the server with the lowest priority number is chosen first. If that server is unavailable, the next server with the next lowest priority number is chosen, and so on. The public FortiGuard servers are only used if the include-default-servers option is enabled and all the custom servers are unavailable.Reference:Fortinet Enterprise Firewall Study Guide for FortiOS 7.2, page 132. In the event of an outage at 10.0.1.240, the FortiGate will choose the next server in the sequence for web filter rating requests, which is 10.0.1.244 according to the configuration shown in the exhibit. This is because the server list is ordered by priority, and the server with the lowest priority number is chosen first. If that server is unavailable, the next server with the next lowest priority number is chosen, and so on. The public FortiGuard servers are only used if the include-default-servers option is enabled and all the custom servers are unavailable.
Reference:
Fortinet Enterprise Firewall Study Guide for FortiOS 7.2, page 132.
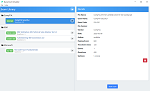
Question 3
Exhibit.
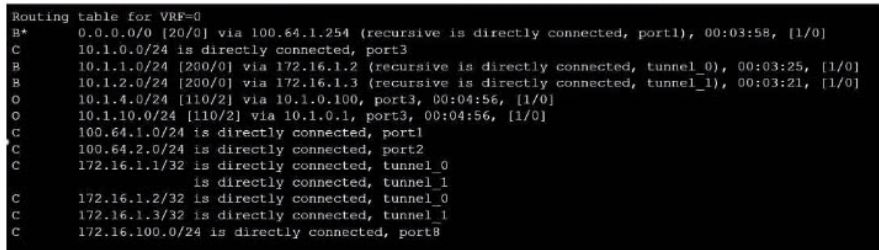
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a partial touting table
What two concisions can you draw from the corresponding FortiGate configuration? (Choose two.)
- IPSec Tunnel aggregation is configured
- net-device is enabled in the tunnel IPSec phase 1 configuration
- OSPI is configured to run over IPSec.
- add-route is disabled in the tunnel IPSec phase 1 configuration.
Correct answer: BD
Explanation:
Option B is correct because the routing table shows that the tunnel interfaces have a netmask of 255.255.255.255, which indicates that net-device is enabled in the phase 1 configuration.This option allows the FortiGate to use the tunnel interface as a next-hop for routing, without adding a route to the phase 2 destination1.Option D is correct because the routing table does not show any routes to the phase 2 destination networks, which indicates that add-route is disabled in the phase 1 configuration.This option controls whether the FortiGate adds a static route to the phase 2 destination network using the tunnel interface as the gateway2.Option A is incorrect because IPSec tunnel aggregation is a feature that allows multiple phase 2 selectors to share a single phase 1 tunnel, reducing the number of tunnels and improving performance3. This feature is not related to the routing table or the phase 1 configuration.Option C is incorrect because OSPF is a dynamic routing protocol that can run over IPSec tunnels, but it requires additional configuration on the FortiGate and the peer device4. This option is not related to the routing table or the phase 1 configuration.Reference:1: Technical Tip: 'set net-device' new route-based IPsec logic22: Adding a static route53: IPSec VPN concepts64: Dynamic routing over IPsec VPN7 Option B is correct because the routing table shows that the tunnel interfaces have a netmask of 255.255.255.255, which indicates that net-device is enabled in the phase 1 configuration.This option allows the FortiGate to use the tunnel interface as a next-hop for routing, without adding a route to the phase 2 destination1.
Option D is correct because the routing table does not show any routes to the phase 2 destination networks, which indicates that add-route is disabled in the phase 1 configuration.This option controls whether the FortiGate adds a static route to the phase 2 destination network using the tunnel interface as the gateway2.
Option A is incorrect because IPSec tunnel aggregation is a feature that allows multiple phase 2 selectors to share a single phase 1 tunnel, reducing the number of tunnels and improving performance3. This feature is not related to the routing table or the phase 1 configuration.
Option C is incorrect because OSPF is a dynamic routing protocol that can run over IPSec tunnels, but it requires additional configuration on the FortiGate and the peer device4. This option is not related to the routing table or the phase 1 configuration.
Reference:
1: Technical Tip: 'set net-device' new route-based IPsec logic2
2: Adding a static route5
3: IPSec VPN concepts6
4: Dynamic routing over IPsec VPN7